Description
What Is Stenabolic (SR9009)?
Stenabolic, also known as SR9009, is a synthetic compound developed to modulate the activity of nuclear receptors REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ. Although frequently mentioned alongside SARMs, SR9009 is not a SARM; rather, it is a unique REV-ERB agonist—a class of regulators involved in controlling circadian rhythm, energy metabolism, and inflammatory responses. SR9009 was designed to study molecular mechanisms related to mitochondrial function, lipid homeostasis, and skeletal muscle adaptations under physical stress.
Mechanism of Action of Stenabolic (SR9009)
Stenabolic acts by activating the REV-ERBα receptor, which regulates transcription of genes responsible for mitochondrial biogenesis, energy substrate utilization, and circadian rhythm alignment. Through this modulation, SR9009 enhances cellular oxidative capacity, reduces lipid synthesis, and suppresses inflammation at the molecular level. This results in improved metabolic efficiency, glucose regulation, and increased muscular endurance. Due to its selective mechanism, SR9009 is considered a compound of high interest for studies in metabolism and chronobiology.
Scientifically Supported Potential Benefits of Stenabolic (SR9009)
SR9009 has been extensively researched in laboratory settings and is associated with a range of potential effects, including:
- Increased mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular energy efficiency;
- Enhanced fat oxidation and reduced lipid accumulation;
- Improved glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity;
- Support for physical endurance through optimized energy utilization;
- Potential reduction of inflammatory markers;
- Modulation of circadian rhythms and cellular metabolic balance.
These effects highlight SR9009’s role as a research compound for investigating chronic metabolic conditions, energy adaptation, and molecular physiology.
Stenabolic (SR9009) vs Other SARMs
Stenabolic (SR9009) is often grouped with SARMs, although it is technically not a SARM. Instead, it is a REV-ERBα agonist involved in regulating circadian rhythms, metabolic function, and mitochondrial activity. Despite this distinction, SR9009 is frequently compared to compounds such as Cardarine (GW501516), Ostarine (MK-2866), and Ligandrol (LGD-4033) due to its role in endurance, lipid metabolism, and recovery-focused research.
Compared to Cardarine (GW501516), both compounds influence metabolic efficiency and fat oxidation. Cardarine activates PPAR-δ receptors, while SR9009 targets REV-ERBα; both encourage the use of fat as an energy source. However, Stenabolic offers a more pronounced impact on circadian regulation, making it unique for research centered on metabolic and sleep rhythm synchronization.
Relative to Ostarine, SR9009 does not demonstrate anabolic effects on muscle mass but supports mitochondrial density and energy efficiency in muscle tissue. While Ostarine focuses on muscle maintenance and development, Stenabolic enhances endurance and metabolic adaptation under stress and load.
When compared to Ligandrol, which has a strong anabolic effect, SR9009 functions as a metabolic modulator rather than a growth stimulant. This positions it as a suitable compound in research protocols that prioritize energy optimization, fat reduction, and improved aerobic capacity over hypertrophy.
Stenabolic holds a distinct position among SARM-like compounds—not by directly activating androgen pathways, but by regulating internal biological rhythms, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial performance.
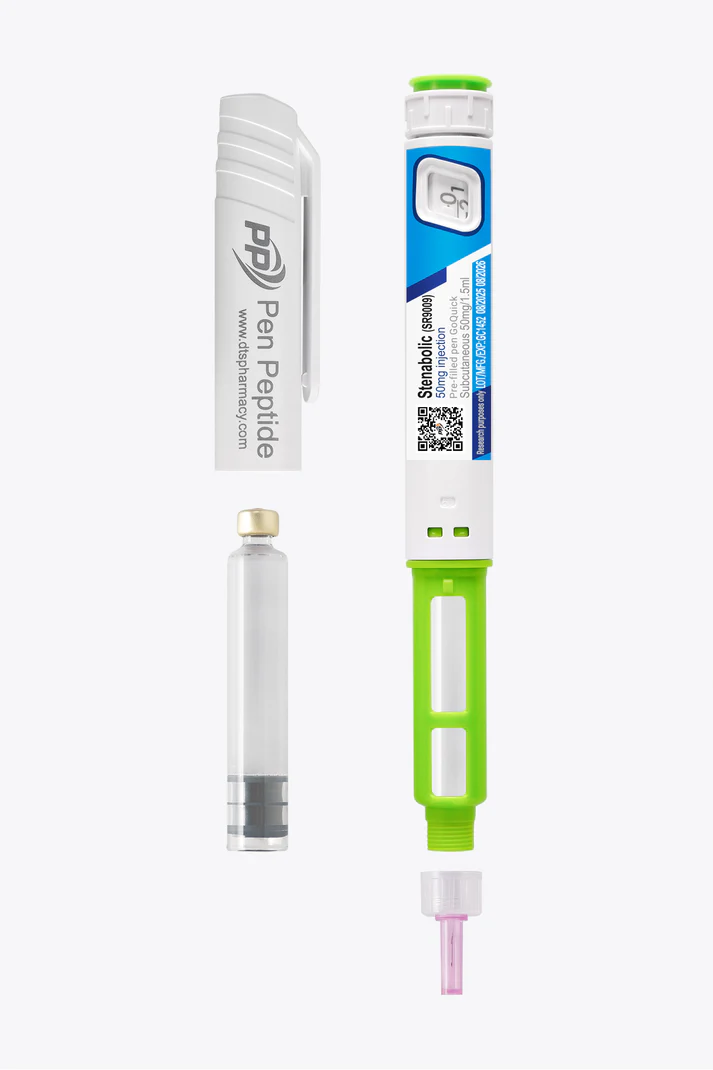
Dosage and Application of Stenabolic (SR9009) in Research Protocols
Suggested research protocol: 7 units once daily for 4–6 weeks, followed by a 2–4 week off-cycle.
1 unit = 33.33mcg
Total pen content: 150 units
Possible Side Effects of Stenabolic (SR9009)
Available scientific data suggests that SR9009 has a complex metabolic profile and should be used with caution. Adverse effects observed in research settings may include:
- Circadian rhythm disruption during prolonged use;
- Limited data on long-term systemic impact and organ interaction.
Proper dosing and control over the duration of use play a critical role in minimizing potential side effects.
For laboratory purposes and personal observation only.