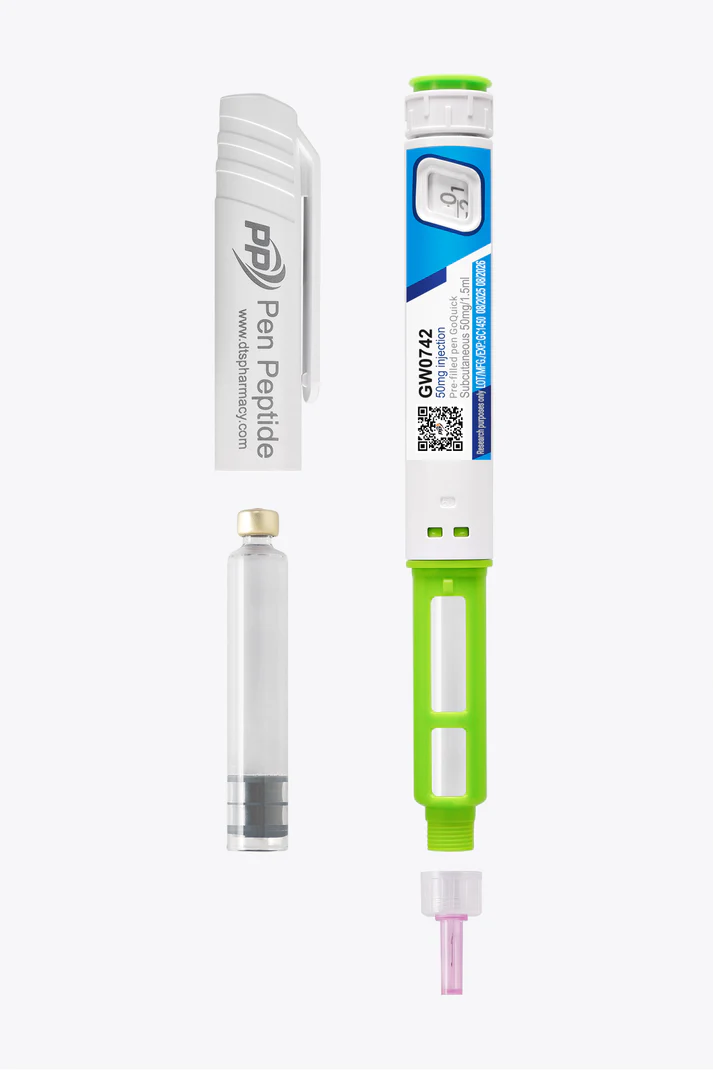
Description
What is GW0742?
GW0742 is a synthetic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR-δ) agonist investigated as a potential regulator of metabolic and energy processes. Structurally related to GW501516, GW0742 exhibits higher selectivity and affinity for PPAR-δ, making it a valuable research target targeting the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism, energy balance, and muscle oxidation. Due to its specific activity, the compound is used in a laboratory environment to analyze molecular mechanisms related to mitochondrial function, metabolic flexibility and physical endurance.
GW0742 Mechanism of Action:
GW0742 binds selectively to PPAR-δ receptors – nuclear receptors involved in the regulation of the expression of genes related to energy metabolism. Activation of these receptors leads to stimulation of fatty acid oxidation, improvement of mitochondrial activity and increase of energy efficiency in muscle tissue. Furthermore, GW0742 modulates glucose homeostasis and affects the lipid profile without directly affecting the hormonal axis. It is this mechanism that makes it particularly interesting in scientific research focused on metabolic diseases, endurance training and energy adaptation.
Potential scientifically supported benefits of GW0742:
GW0742 has been the subject of a number of analyzes in which the following potential effects have been observed:
- Increased fat burning by stimulating β-oxidation;
- Increased mitochondrial activity and energy efficiency in muscles;
- Improved glucose sensitivity and glycemic control;
- Potentially supporting physical endurance;
- Anti-inflammatory modulation through regulation of PPAR-δ dependent pathways;
- Maintaining a healthy lipid profile.
Due to these observations, GW0742 is frequently included in protocols for the study of metabolic disorders, sports physiology and cardiometabolic mechanisms.
Comparison of GW0742 with other SARMs and metabolic agonists
GW0742 is a synthetic PPAR-δ (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta) agonist that is not a SARM, but is often grouped with them due to its similar use in metabolic regulation, lipid control, and endurance research protocols. It is most commonly compared to Cardarine (GW501516), Stenabolic (SR9009) and sometimes to lighter SARMs such as Ostarine (MK2866) when combined for body recomposition purposes.
Compared to Cardarine, GW0742 has a higher affinity for the PPAR-δ receptor, making it more potent in models investigating fat oxidation and improvement of mitochondrial function. Both molecules promote the use of fat as a primary energy source, but GW0742 is often preferred in more targeted metabolic studies, especially when a more selective effect on energy metabolism in muscle tissue is sought.
Compared to Stenabolic (SR9009), which acts by activating REV-ERBα and affecting circadian rhythms, GW0742 is more focused on the deep regulation of lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis, without directly affecting the biological clock. While SR9009 improves energy capacity and endurance through mitochondrial activity, GW0742 does so by activating metabolic genes responsible for fatty acid oxidation.
In the context of SARMs such as Ostarine or Ligandrol, which affect muscle mass through androgen receptors, GW0742 stands out as a completely non-hormonal metabolic modulator suitable for studies where the goal is fat burning, improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic flexibility.
Dosage and administration of GW0742 in research protocols:
Recommended study schedule: 5-6 units once daily for 4-6 weeks, followed by a 2-4 week rest period.
1 unit = 33.33mcg.
Total quantity in pen: 150 units
Possible side effects of GW0742:
While GW0742 shows promising results, it is important to consider its safety profile. Its observed negative effects include:
- Changes in lipid metabolism during long-term use;
- Lack of long-term data on chronic exposure;
- Adverse interactions with other PPAR-modulating compounds.
Adherence to the optimal dosage and control of the duration of application play a key role in limiting the occurrence of side effects.
For laboratory purposes and personal observation only.